 |
Fragment Based Screening by Experimental Drug Development Centre (EDDC) |
Fragment Based Screening (FBS) is a validated approach towards finding high quality hits against challenging proteins that are classified as undruggable. A team of experts at the FBS employ proprietary library and a cascade of biophysical techniques, to find ligand efficient fragment hits against targets in the oncology and infectious disease space. The fragment library @ FBS covers a wide range of chemical spaces and is suitable for diverse targets such as DNA Gyrase and undruggable targets such as protein-protein interactions. The screening methods are able to identify fragments binding weakly to the target (affinity in mM range). EDDC has diverse methodologies to monitor fragment growth, which can be achieved through measuring binding affinities, activities or competition assays. In summary, FBS offers expertise for projects involving fragment identification using binding and competition assays, characterization of protein-fragment interactions, map the ligand binding site, designing fragment growth and target-lead interactions. |
Key Services |
|
|
|
|
Expertise in Diverse Targets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Technologies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
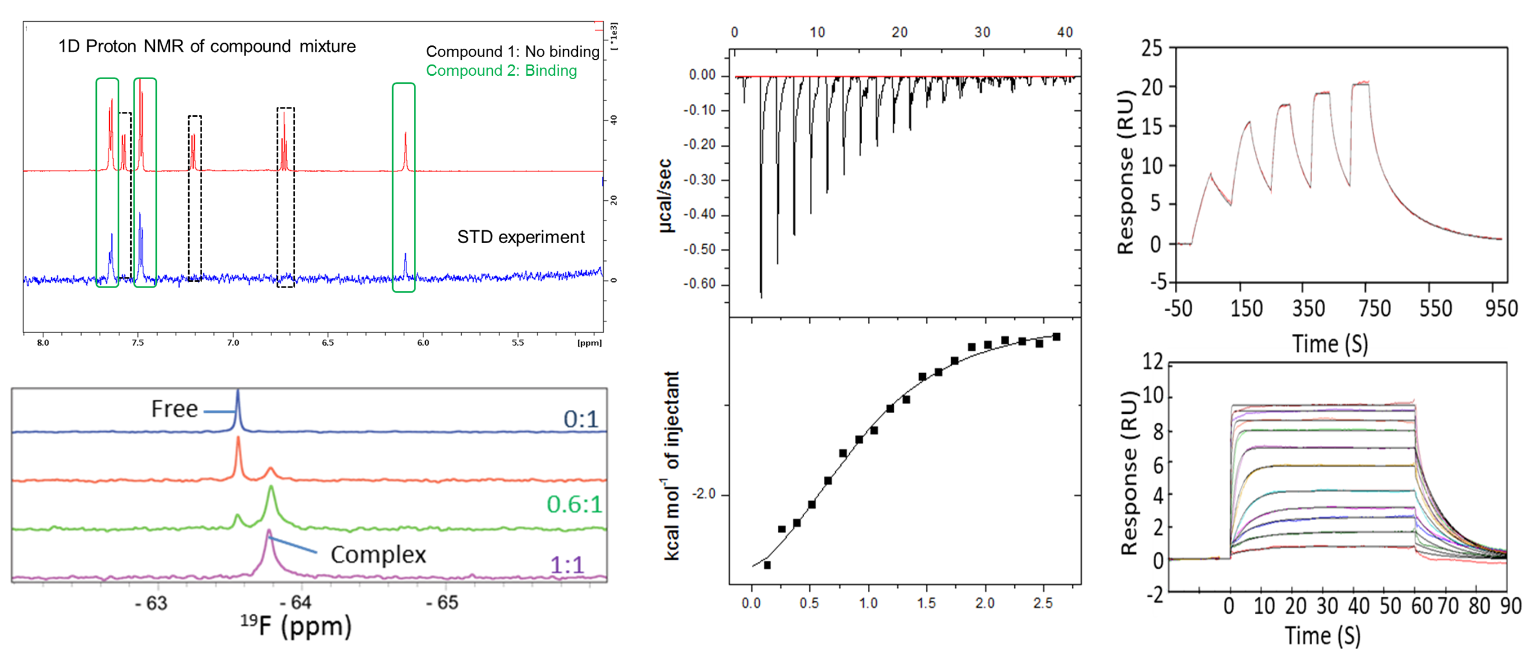 |
Different types of methods are available to probe target-ligand interactions. Protein-observed and ligand observed solution NMR experiments are utilized to screen fragments, confirm fragment hits identified using other methods and map the fragment bind sites for certain targets with a molecular weight less than 30 kDa. This figure shows the application of STD-NMR and 19F-NMR in fragment screening and hit confirmation. |
 |
| Some of the research publications produced by EDDC FBS |

